An odometer reading reveals the journey every vehicle undertakes. Typically displayed in kilometers (km) or miles (mi), it serves as a crucial metric in fleet management. This number encapsulates vehicle usage, wear and tear, and overall efficiency. Modern fleets harness the power of telematics and vehicle sensors to gather these readings automatically. This technology guarantees accuracy while eliminating the hassle of manual logging.
Why Odometer Readings Matter in Fleet Management
Odometer readings may appear simple, yet they are the heartbeat of every fleet. These numbers shape maintenance schedules, impact asset valuation, fuel efficiency tracking, driver management, and compliance reporting. Let’s dive deeper into the significance of odometer readings.
Maintenance scheduling
Fleet managers rely on odometer readings to time preventive maintenance just right. Service intervals—from oil changes to brake inspections—hinge on those vital mileage milestones. By keeping detailed records of these numbers, fleets dodge costly breakdowns and extend vehicle lifespans.
For example, if a company sets maintenance at every 15,000 km, an automatic alert from the fleet management system can notify the maintenance team once a vehicle reaches that threshold.
Fuel Efficiency Tracking
Odometer data, combined with fuel consumption records, helps calculate miles per gallon (MPG) or liters per 100 kilometers (L/100km). This data identifies underperforming vehicles or drivers with inefficient driving habits. When tracked over time, it reveals trends in fuel economy, helping to optimize routes and reduce overall operating costs.
Depreciation & Resale Value
Mileage is a critical factor in determining a vehicle’s resale value and total cost of ownership (TCO). The higher the odometer reading, the lower the resale value tends to be. Accurate odometer tracking enables fleet owners to plan vehicle replacement cycles in a way that maximizes return on investment (ROI).
Regulatory Compliance
Many jurisdictions require regular odometer reporting for compliance, taxation, and audits. For example, fleets that operate across borders (like under the International Fuel Tax Agreement — IFTA) must submit accurate mileage data for tax purposes. Reliable odometer data ensures that your company remains compliant with such regulations.
Usage-Based Billing
In leased or shared fleets, billing often depends on the actual distance traveled. Automated odometer readings simplify invoicing by providing precise usage data—improving fairness, transparency, and accuracy for all parties involved.
Driver Accountability & Route Management
Tracking odometer readings can also help verify driver-reported mileage and detect route deviations. Discrepancies between planned route distance and odometer data can highlight route inefficiencies, unauthorized trips, or potential misuse of fleet assets.
Example in Practice
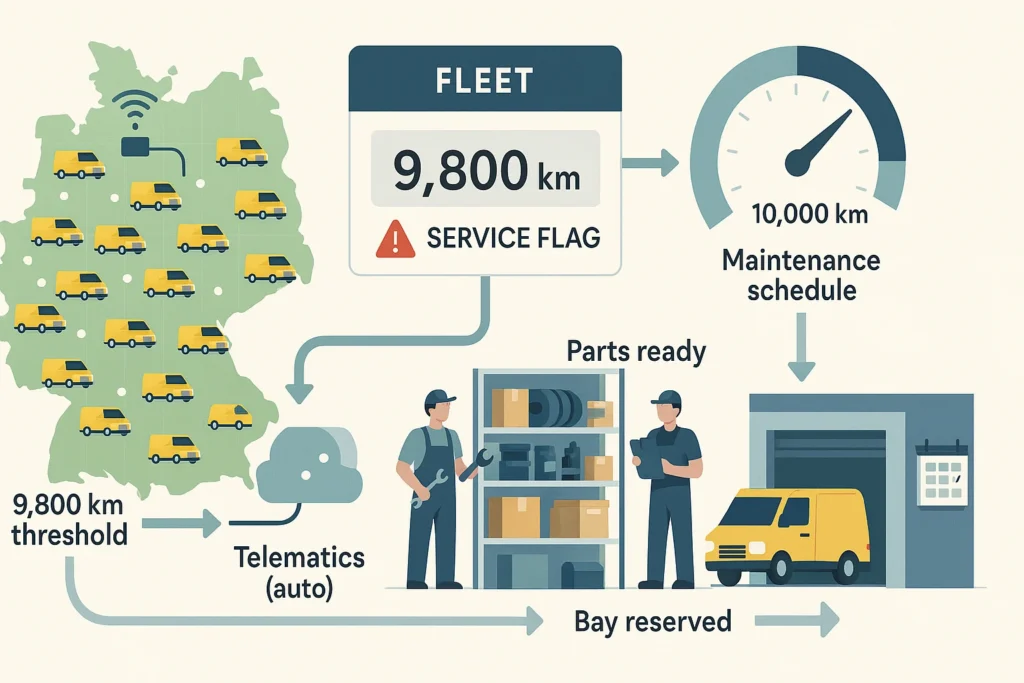
Let’s consider a real-world scenario: A logistics company operates 40 delivery vans across Germany. Each van has a maintenance schedule every 10,000 km.
Their fleet management software collects odometer readings through a telematics device installed in each vehicle without human intervention. When a van reaches 9,800 km, the system flags it for service scheduling. The maintenance team prepares parts and reserves workshop time before the vehicle even arrives.
By monitoring odometer readings digitally, the company:
Avoids costly breakdowns due to missed maintenance.
Extends the average vehicle lifespan by 20%.
Reduces downtime by scheduling services in advance.
Improves accuracy in fuel and cost tracking.
This data-driven approach transforms the odometer from a simple dashboard number into a powerful management tool.
Modern Odometer Tracking Technologies
Today’s fleets no longer rely on manual readings. Instead, telematics systems automatically record and transmit odometer data in real time.
These systems connect to the vehicle’s OBD-II or CAN bus port, capturing accurate mileage alongside engine diagnostics, GPS location, and driver behavior metrics. The data syncs with the Fleet Management System (FMS), providing instant visibility into the status of each vehicle.
Benefits include:
-
-
Automated accuracy – No manual data entry errors.
-
Real-time insights – Detects usage patterns and predicts maintenance needs.
-
Integration with reports – Connects mileage data to cost, driver, and performance analytics.
-
Preventing Unauthorized Odometer Changes
Odometer manipulation isn’t just a nuisance—it’s illegal in many jurisdictions and can jeopardize maintenance schedules, warranty standing, usage-based billing, and compliance reporting. Below is a practical, layered approach fleets can use to deter, detect, and document any attempts to alter mileage.
The risk surface (why this happens)
Financial gain: Lower mileage raises resale value and can mask excess wear. In the U.S., odometer fraud is a federal crime and affects hundreds of thousands of vehicles annually, costing consumers over $1B each year.
Gaps in process: Manual entry, spreadsheet copies, and weak access controls invite “harmless corrections” that become hard-to-trace rollbacks.
Electronic attack paths: Modern odometers are electronic. Unsecured diagnostic ports, weak device security, or poorly monitored data pipelines can be abused to push falsified readings. Standards like ISO/SAE 21434 exist because vehicle E/E systems require cybersecurity controls across their lifecycle.
Detection & alerting (assume attempts will occur)
Regression flags: Alert if a reading decreases versus last known value, or if mileage growth is implausibly low versus GPS-measured distance.
Cross-source reconciliation: Compare telematics odometer to:
distance accumulated from GPS odometry,
shop/service readings, and
inspection logs (in the EU, periodic roadworthiness tests record mileage and help expose tampering).
Anomaly analytics: Watch for sudden step-downs (e.g., –30,000 km overnight), device disconnects near edits, or edits clustered by the same user.
Tamper events: Trigger alerts if a device is unplugged, loses power unexpectedly, or its enclosure is opened.
A practical policy you can adopt this week
Default to automatic readings from approved telematics; disable manual entry for day-to-day use.
Set guardrails:
Block saves if new odometer < prior odometer (unless “cluster replacement” workflow is used).
Alert on abnormal deltas (e.g., >10% deviation from GPS distance over 7 days).
Require evidence for exceptions: Photo of dashboard + service paperwork for any correction; second-person approval.
Reconcile monthly: Telemetrics vs GPS-distance vs maintenance/inspection records; investigate variances.
Capture tamper signals: Turn on unplug/open tamper events in your devices and route them to notifications/SIEM.
Review legally required disclosures (U.S. Part 580; EU inspection certificates) and keep them with each vehicle’s record.